Addiction is very common, but very hidden
Drug and alcohol use, abuse, and addiction continue to be among the nation’s leading public health problems.
In 2022…
48.7 Million
people over age 12 had a substance abuse disorder in the past year
This includes:
29.5 million who had an alcohol use disorder (AUD) 27.2 million who had a drug use disorder (DUD), and 8.0 million people who had both.
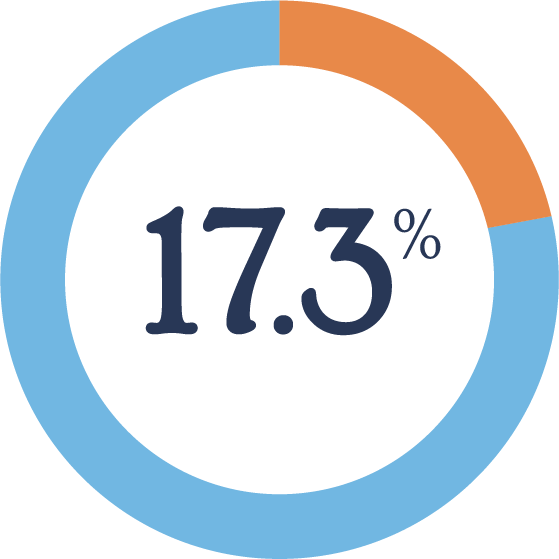
In comparison…
Substance Use Disorder
17.3%
Cancer
6.1%
Heart Disease
5.5%
Types of Substance Use Disorders
Alcohol
Caffeine
Hallucinogens (LSD, MDMA, Ecstasy)
Stimulants (Cocaine, Ritalin, Methamphetamine)
Inhalants
Cannabis (Marijuana)
Opioids (Pain Killers, Heroin)
Tobacco
Sedatives, Hypnotics, or Anyxiolytics (Valium, Xanax, "Qualudes")
Behavior is How Substance User Disorders are Diagnosed
Regardless of the particular substance, the diagnosis of a substance use disorder is based upon a pathological set of behaviors related to the use of that substance. These disorders are categorized into three levels of severity. The DSM-5 States That:
Mild
substance use disorder is a presence of 2-3 symptoms listed below
Moderate
substance use disorder is a presence of 4-5 symptoms listed below
Severe
substance use disorder is a presence of 6+ symptoms listed below
01
Impaired Control
Impaired control may be evidenced in several different ways:
Using for longer periods of time than intended, or using larger amounts than intended
Wanting to reduce use, yet being unsuccessful in doing so
Spending excessive time getting/using/recovering from drug or alcohol use
Cravings that are so intense it is difficult to think about anything else
02
Risky Use
The key issue of this criteria is the failure to refrain from using the substance despite the harm it causes
Addiction may be indicated when someone repeatedly uses substances in physically dangerous situations including operating machinery or driving a vehicle.
Some individuals continue to use substances even though they are aware it is causing or worsening physical or psychological problems.
03
Social Impairment
Social impairment is one type of substantial harm (or consequence) caused by the repeated use of a substance
People may continue to use despite problems with work, school, or family/social obligations. This may include repeated work absences, poor school performance, neglect of children, or failure to meet household responsibilities
People may continue to use despite having interpersonal problems because of their use. This could include arguments with family members about the use or losing relationships because of continued use
Important and meaningful social and recreational activities may be given up or reduced because of their continued use. A person may spend less time with their family or friends, or even engaging in personal hobbies, due to their use
04
Pharmacological Indicators (tolerance/withdrawal)
Tolerance and withdrawal can be classic indicators of an advanced substance abuse problem which also makes them important concepts
Tolerance occurs when people need to increase the amount of a substance they are using to achieve the same desired effect. In other words: once someone has been using a substance repeatedly for an extended period of time they begin to build a tolerance for that substance which in return creates the need and desire to use more. People experience tolerance differently depending on the amount of use, length of use, and substance being used.
Withdrawal is the cluster of symptoms that occur when an individual suddenly stops using or decreases their intake of substances. Withdrawal symptoms can vary significantly depending on the individuals tolerance and the substance being used. Withdrawal symptoms can be very unpleasant and depending on the drug (including alcohol), withdrawals can be fatal. Therefore, it is important to consult with a medical professional before attempting to stop drug or alcohol use after a period of heavy, continuous use.
What does treatment and recovery consist of?
Treatment for substance use disorders consists of multiple components including:
Outpatient Treatment
Intensive Outpatient Treatment
Inpatient Residential Treatment
Medication-Assisted Therapy (Vivitrol, Antabuse, Naltrexone)
Peer Support (Family, Friends, Fellowship)
12-Step Process
Self-Help Meetings
Volunteer/Community Service
Spirituality/Faith Related Activities
Looking for more?
Click to download PDFs for more general information about treatment and recovery.